Cytochalasin D: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Kevin Created page with "*[http://www.xenbase.org/literature/article.do?method=display&articleId=50776 Piper et al., 2015]" |
imported>Kevin No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Description== | |||
syn CytoD | |||
inhibits neuronal growth cone | |||
"Cytochalasin D is a cell permeable fungal toxin that binds to the barbed end of actin filaments inhibiting both the association and dissociation of subunits. This compound causes the disruption of actin filaments and inhibition of actin polymerization." | |||
*-Thermo Scientific Product Description | |||
[[File:cytochalasinD.png|frame|right|cytochalasin D structure, photo from Sigma-Aldrich]] | |||
==Genes Affected== | |||
==Suppliers== | |||
*[https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/PHZ1063 Molecular Probes] | |||
==Usage Notes== | |||
==References== | |||
*[https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5458428 Pubchem] | |||
*[http://www.xenbase.org/literature/article.do?method=display&articleId=11687 Lautermilch et al., 2000] | |||
*[http://www.xenbase.org/literature/article.do?method=display&articleId=50776 Piper et al., 2015] | *[http://www.xenbase.org/literature/article.do?method=display&articleId=50776 Piper et al., 2015] | ||
>929 Xenbase articles contain a reference to cytochalasin according to [http://www.xenbase.org/cgi-bin/textpresso/xenopus/search textpresso] | |||
* | |||
*[[Small Molecules for Xenopus Research|Back To Small Molecules Home Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:55, 13 October 2015
Description
syn CytoD inhibits neuronal growth cone "Cytochalasin D is a cell permeable fungal toxin that binds to the barbed end of actin filaments inhibiting both the association and dissociation of subunits. This compound causes the disruption of actin filaments and inhibition of actin polymerization."
- -Thermo Scientific Product Description
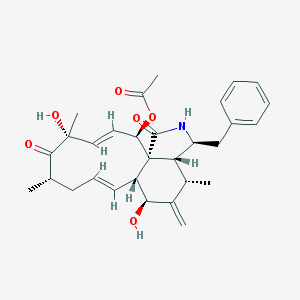
Genes Affected
Suppliers
Usage Notes
References
>929 Xenbase articles contain a reference to cytochalasin according to textpresso